Are you a fitness geek who's interested in opening up a gym? This guide will tell you all you need to know about this. Let's begin!
Steps to Open a Gym
Opening a gym can be a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Here are some general steps you can follow to open a gym:
1. Planning and research
To find out whether a gym is needed in your community, conduct market research. Incorporate your target market, the competition, the services you offer, financial projections, and marketing strategies in your business plan.
2. Location
Pick a place that is convenient to get to and has enough parking. Take into account the room's dimensions, configuration, and required equipment.
3. Legal and regulatory requirements
Secure the authorizations and licenses required to run a gym in your region. This can entail having your company registered, getting liability insurance, and adhering to construction requirements and safety rules.
4. Financing
Establish the financial requirements for opening your gym and seek funding via investments, loans, or grants.
5. Supplies and equipment
Invest in or rent weights, aerobic equipment, and exercise mats. Supplies like cleaning products, towels, and water bottles will also need to be purchased.
6. Staffing
Hire qualified workers, such as front desk agents, group exercise instructors, and personal trainers. Be sure you abide by all rules and laws pertaining to work.
7. Marketing
Create a marketing plan to advertise your gym and draw customers. This can entail setting up a website, social media profiles, and local media advertising.
8. Grand opening
Host a grand opening event to introduce your gym to the community and offer promotions to attract new members.
9. Ongoing operations
After your gym opens, keep track of and oversee operations to guarantee success. To keep members interested, this means keeping up with equipment maintenance, offering top-notch customer service, and introducing new programs and services.
What Are Some Skills and Experiences That Will Help You Build a Successful Gym?
There are several skills and experiences that can help you build a successful gym, including:
1. Fitness knowledge: The foundation of a successful gym is a solid grasp of fitness and exercise. This includes understanding various exercise forms, training methods, and apparatus.
2. Business management: Managing a gym needs a variety of business abilities, such as budgeting, marketing, and personnel control.
3. Sales and customer service: You need to be able to sell your gym's services and offer first-rate customer service to draw in new members and keep them coming back.
4. Marketing and branding: A strong brand and successful marketing for your gym will help you attract new members and cultivate a devoted clientele. Leadership and management: As a gym owner, you will need to lead and manage a team of staff to ensure the smooth operation of the business.
5. Networking: Staying updated on the newest trends and opportunities can be made easier by cultivating connections with other companies and experts in the fitness sector.
6. Entrepreneurial spirit: Establishing a profitable gym demands ingenuity, risk-taking, and an entrepreneurial spirit.
7. Fitness-related personal experience: Having fitness-related personal experience will help you relate to your consumers and comprehend their requirements and ambitions.
8. Technical abilities: Knowledge of technology and software for administering the gym, as well as the ability to handle and maintain workout equipment, can be helpful qualities for managing a successful gym. Passion for fitness and helping others: Finally, having a genuine passion for fitness and a desire to help others achieve their fitness goals can be a key ingredient for building a successful gym.
9. Technical know-how: Running a successful gym requires handling and maintaining workout equipment and having a working grasp of technology and management software.
10. Passion for fitness and helping others: Finally, having a genuine passion for fitness and a desire to assist others in achieving their fitness goals can be a crucial component in creating a successful gym.
Growth Potential for a Gym
The growth potential for a gym depends on several factors, including its location, target market, services offered, and the overall demand for fitness services in the area. Here are some factors that can impact a gym's growth potential:
1. Location: Compared to a gym in a remote or difficult-to-find location, one in a high-traffic region with good visibility and simple access will likely have a larger growth potential.
2. Target market: A gym that targets a certain group of people, such as athletes, the elderly, or solely women, may have a more devoted and focused clientele.
3. Services provided: By providing various services, like personal training, group exercise classes, and nutrition counseling, a business can draw in a wider spectrum of clients and perhaps boost revenue.
4. Competitive landscape: The number and quality of competing gyms in the area can impact a gym's potential for growth. Industry trends: Keeping up with trends in the fitness industry, such as new types of workouts or wellness services, can help a gym stay relevant and attract new customers.
5. 5. Marketing: A gym can expand its member base and attract new clients by using effective marketing methods.
6. 6. Customer retention: Retaining existing customers through excellent customer service and engagement can help a gym grow through word-of-mouth referrals and positive reviews.
What are The Costs Involved in Opening a Gym?
The costs involved in opening a gym can vary widely depending on factors such as the location, size, type of gym, and equipment needed. Here are some of the common costs to consider when opening a gym:
1. Lease or rent: Depending on the location and size of the gym, the cost of leasing or renting a space might vary substantially.
2. Equipment: Depending on the type and amount required, the price of a gym's equipment can range from a few thousand dollars to hundreds of thousands of dollars.
3. Renovations: Depending on the state of the facility, upgrades may be required to make the gym usable. This can apply to plumbing, electrical, lighting, and flooring projects.
4. Licenses and permits: Acquiring the licenses and permits required to run a gym may require paying fees and incurring legal costs. Insurance: Liability insurance is essential for protecting the gym in case of accidents or injuries.
5. Staffing: Hiring new employees can be expensive for a gym due to pay, benefits, and training costs.
6. Marketing and advertising: Expenses for marketing and advertising may include creating websites, utilizing social media, and running print or online advertisements.
7. Software and technology: Booking software, gym management software, and other technology can help operations run more smoothly, but they may also be more expensive.
8. Utilities and maintenance: Ongoing costs like electricity, materials for cleaning, and equipment maintenance can pile up over time.
What are the Ongoing Expenses of Running a Gym?
Running a gym involves ongoing expenses that should be taken into consideration when planning and budgeting. Here are some common ongoing expenses of running a gym:
1. Rent or mortgage: One of the major continuous costs is the price of renting or buying the gym space. Lease payments, property taxes, and mortgage payments all fall under this category.
2. Utilities: A gym's continuing expenses must include the cost of utilities like power, water, gas, and internet.
3. Equipment maintenance and repair: It's critical to do routine maintenance and repair of gym equipment to ensure both user safety and equipment longevity. Budgeting for this continuous expense is advisable.
4. Janitorial and cleaning services: A clean gym is necessary to maintain a secure and hygienic atmosphere. Janitorial and cleaning costs are recurring expenses. Staff salaries and benefits: Staffing costs, including salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes, are an ongoing expense for a gym.
5. Staff salaries and benefits: A gym's continuing costs for personnel include salaries, insurance, and payroll taxes.
6. Marketing and advertising: Continuous marketing and promotion activities are required to draw in new clients and keep existing ones. These expenses might cover print ads, social media marketing, email promotions, and more.
7. Insurance: Liability and property insurance are recurring costs to safeguard the gym against conceivable claims and harm.
8. Supplies: An recurring cost for a gym is the purchase of necessary supplies, including towels, cleaning materials, and office supplies.
Who is The Target Market?
The target market for a gym can vary depending on the gym's location, size, services offered, and other factors. Here are some common target markets for gyms:
1. Fitness enthusiasts: These people are already committed to health and fitness and are seeking a top-notch gym with various tools and services to assist them in achieving their fitness objectives.
2. Beginners: For people who are just beginning their fitness adventure, a gym that caters to beginners may provide introductory classes, personal training, or a more helpful and encouraging environment.
3. Athletes: Some gyms have a dedicated section for athletes and may provide them with specialized tools, training plans, and coaching services to help them perform better.
4. Women: In recent years, women-only gyms have grown in popularity, providing a safe and encouraging setting for women to exercise without feeling self-conscious.
5. Seniors: To accommodate the needs of older people, gyms that cater to elders may offer low-impact exercises, classes just for seniors, and specialized equipment.
6. Families: To promote healthy behaviors for the entire family, family-friendly gyms may provide daycare services, family-friendly classes, and kid-friendly activities.
Ultimately, the target market for a gym will depend on the gym's unique value proposition and the needs and preferences of the local community. It's important for gym owners to research and understand their target market to effectively market their gym and provide the services that their customers are looking for.
How Does a Gym Make Money?
A gym makes money by generating revenue from its members and other sources. Here are some common ways that a gym can make money:
1. Membership fees: The primary source of revenue for most gyms is membership fees. Members pay a monthly or annual fee to access the gym's facilities, equipment, and services.
2. Personal training: Many gyms offer personal training services, either through in-house trainers or independent contractors. Personal trainers typically charge an hourly rate or package fee for their services, and the gym may take a percentage of the fee as a commission.
3. Group fitness classes: Group fitness classes such as yoga, spin, or HIIT can be a popular service for gym members. These classes may be included in the membership fee, or members may need to pay an additional fee to attend.
4. Retail sales: Many gyms sell fitness apparel, supplements, and other fitness-related products to their members, either in-house or through partnerships with other retailers.
5. Corporate partnerships: Some gyms partner with corporations to offer discounted membership rates to their employees as part of a wellness program.
6. Event rentals: Gyms may rent out their facilities for events such as fitness competitions, charity events, or private parties.
7. Personal locker rentals: Some gyms offer personal locker rentals as an additional service to members.
How Much Can You Charge Customers?
The amount a gym can charge its customers will depend on various factors such as the location, size, type of gym, equipment offered, and the level of service provided. Here are some key factors that can affect the pricing of gym memberships:
1. Location: The cost of living and competition in the local market can impact how much a gym can charge for its services.
2. Type of gym: The type of gym can impact pricing. For example, a luxury gym that offers high-end amenities such as spa services and personal training may charge a premium price compared to a no-frills gym.
3. Equipment and amenities: The type and quantity of equipment and amenities offered can impact pricing. A gym with a wide range of high-quality equipment and modern amenities may charge more than a gym with basic equipment.
4. Level of service: Gyms that offer personalized services such as personal training, nutrition coaching, and customized workout plans may charge more than gyms that offer standard services.
5. Membership term: Gyms may offer different pricing options based on the length of the membership term. For example, a gym may offer a discount for an annual membership compared to a monthly membership.
Overall, the pricing for gym memberships can vary widely. Monthly membership fees can range from $20 to over $200, depending on the factors mentioned above.
It's important for gym owners to research the local market and understand their target market's willingness to pay when setting their prices. It's also important to regularly evaluate pricing and adjust it as necessary to remain competitive and sustainable.
What are the Limitations of Opening a Gym
While opening a gym can be a great opportunity, there are also some limitations to consider. Here are some potential limitations of opening a gym:
1. High start-up costs: Opening a gym can require significant upfront costs, including equipment purchases, rent or building costs, staffing expenses, marketing and advertising costs, and more.
2. Competitive market: Depending on the location, the gym industry can be highly competitive, with many established players already in the market.
3. Maintenance and repair costs: Gym equipment can be expensive to maintain and repair. Regular upkeep is necessary to ensure customer safety and satisfaction.
4. Liability and insurance costs: Gyms must carry insurance to protect against injury or damage claims. The cost of insurance can be significant depending on the size of the gym and the number of employees.
5. Seasonality: The demand for gym services can be seasonal, with fewer customers during certain times of the year, such as during the holidays or summer months.
6. Changing consumer preferences: The fitness industry is always evolving, and consumer preferences can shift quickly. Keeping up with these changes and offering the latest trends and services can be challenging and expensive.
7. Staffing challenges: Finding and retaining qualified staff, particularly personal trainers and other fitness professionals, can be difficult and can impact the quality of services offered.
Potential gym owners need to consider these limitations and thoroughly research and plan for the costs and challenges of opening a gym. By carefully considering these factors and developing a solid business plan, it is possible to overcome these limitations and build a successful gym.
How to Limit the Costs of Opening a Gym?
Opening a gym can be costly, but some strategies can help limit costs. Here are some ways to reduce the costs of opening a gym:
1. Start small: Consider starting with a smaller space or renting a gym space during off-peak hours. Starting with a smaller space can reduce rent, equipment, and utility costs.
2. Buy used equipment: Look for used equipment instead of purchasing new equipment. Many gym owners sell their equipment when they close their businesses or upgrade their facilities.
3. Negotiate with vendors: Negotiate with vendors, such as equipment suppliers, to get the best deals on equipment and supplies.
4. DIY marketing: Consider doing your own marketing, such as social media posts and email newsletters, instead of hiring a marketing agency.
5. Use freelancers or contractors: Consider using freelancers or independent contractors for services such as cleaning, maintenance, and personal training. This can help reduce staffing costs.
6. Offer basic amenities: Consider offering basic amenities such as showers and changing rooms, but avoid offering unnecessary luxury amenities that can increase costs.
7. Get creative with financing: Consider using alternative financing options, such as crowdfunding, loans, or partnerships, to fund your gym.
Overall, it's important to carefully consider costs and to develop a solid business plan that includes strategies to reduce costs without compromising the quality of the gym's services. By taking a lean approach and making smart decisions, it's possible to open a successful gym with minimal costs.
How Can You Cater to Disabled People in Your Gym?
Catering to disabled people in a gym can be a great way to create an inclusive environment and provide fitness opportunities to people with disabilities. Here are some ways to cater to disabled people in your gym:
1. Provide wheelchair accessibility: Ensure your gym is accessible for wheelchair users by providing ramps, wider doorways, and accessible parking spaces.
2. Offer adaptive equipment: Consider offering adaptive equipment such as hand cycles, arm ergometers, or other equipment that can be used by people with disabilities.
3. Hire knowledgeable staff: Hire knowledgeable staff who are trained to work with people with disabilities and can assist with modifications and adaptations to exercises.
4. Offer modifications and adaptations: Work with members with disabilities to offer modifications and adaptations to exercises to ensure that everyone can participate in fitness activities.
5. Provide space for therapy and rehabilitation: Consider offering space for physical therapy and rehabilitation to accommodate the specific needs of people with disabilities.
6. Offer group fitness classes for people with disabilities: Offer specialized group fitness classes for people with disabilities, such as yoga, adaptive aerobics, and wheelchair basketball.
7. Partner with disability organizations: Partner with local disability organizations to provide fitness opportunities and promote your gym to the disability community.
Overall, catering to disabled people in a gym requires a commitment to accessibility and inclusivity. By providing adaptations, knowledgeable staff, and specialized fitness opportunities, you can create an environment that welcomes all people, regardless of their abilities. This way, you can also pitch in your share in helping the community.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, owning a gym can be a rewarding and potentially profitable business venture. However, it requires careful planning, budgeting, and management to succeed. Some important factors to consider when opening a gym include the location, target market, competition, start-up costs, ongoing expenses, and potential profits. It's also essential to focus on creating an inclusive and welcoming environment that caters to a diverse range of customers, including those with disabilities. With the right strategies in place, a gym can attract and retain members, generate revenue, and contribute to the health and wellness of the community.
 Although the formulas for determining your ideal fat ratio are still controversial in the medical and fitness world, we share the two most commonly used measurement parameters below to get an average figure:
Although the formulas for determining your ideal fat ratio are still controversial in the medical and fitness world, we share the two most commonly used measurement parameters below to get an average figure:







 In Turkish cuisine, sufficient protein intake from various sources is provided in almost every region. So it can already be found in your diet, but the protein in your diet may be from weaker and unhealthy sources (fatty red meat, processed foods, etc.). So first choose to go for healthy protein sources. Remember that your protein requirement depends on your age, gender, and how active you are.
In Turkish cuisine, sufficient protein intake from various sources is provided in almost every region. So it can already be found in your diet, but the protein in your diet may be from weaker and unhealthy sources (fatty red meat, processed foods, etc.). So first choose to go for healthy protein sources. Remember that your protein requirement depends on your age, gender, and how active you are.

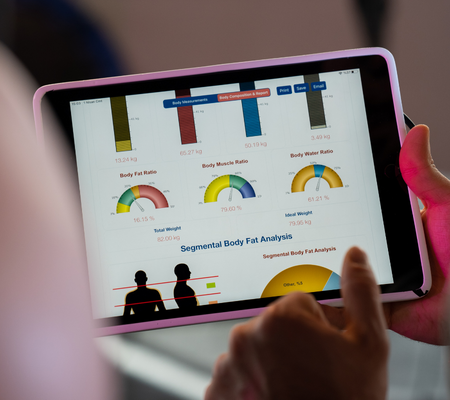
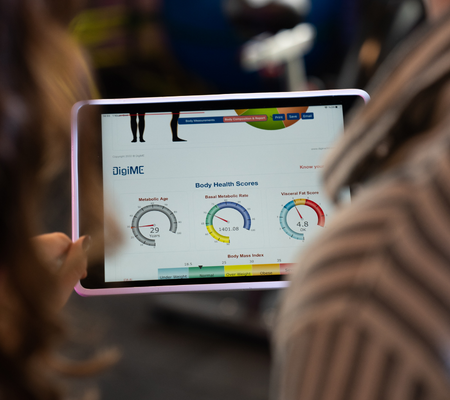
 In the BIS method, on the other hand, the patient is under continuous measurement (for devices that measure at short intervals, such as 5 seconds). Thus, a medical interpretation can be made about the body water percentage.
In the BIS method, on the other hand, the patient is under continuous measurement (for devices that measure at short intervals, such as 5 seconds). Thus, a medical interpretation can be made about the body water percentage.






 It is the daily minimum energy or calorie level when your body is at rest (including sleep) to work effectively. It is the sum of the amount of energy required for significant vital actions such as nerve functions, brain functions, cell renewal and growth, body temperature control, blood circulation, and breathing. The basic metabolic rate is 65-75% of the daily calorie consumption, and the remaining 25-35% is the daily physical activity.
It is the daily minimum energy or calorie level when your body is at rest (including sleep) to work effectively. It is the sum of the amount of energy required for significant vital actions such as nerve functions, brain functions, cell renewal and growth, body temperature control, blood circulation, and breathing. The basic metabolic rate is 65-75% of the daily calorie consumption, and the remaining 25-35% is the daily physical activity.
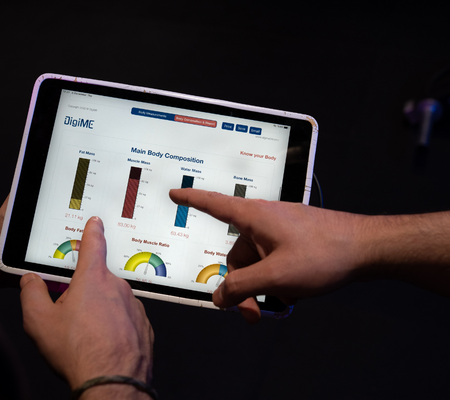












 Strength training is a crucial component of any well-rounded fitness routine. Beyond building muscles and achieving a sculpted physique, strength training offers numerous health benefits that can enhance your overall well-being. In this blog post, we will explore eight ways strength training can benefit your health and provide practical tips to help you get started on your strength training journey.
Strength training is a crucial component of any well-rounded fitness routine. Beyond building muscles and achieving a sculpted physique, strength training offers numerous health benefits that can enhance your overall well-being. In this blog post, we will explore eight ways strength training can benefit your health and provide practical tips to help you get started on your strength training journey.





 There are many different methods for weight loss, but running is an effective and enjoyable way to achieve this goal. Running increases calorie burn, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts overall fitness levels. In this blog post, we will discuss how to incorporate running into your weight loss journey and important factors to consider. Additionally, we will emphasize the importance of a healthy diet, the calories burned during running, workouts, and the significance of strength training.
There are many different methods for weight loss, but running is an effective and enjoyable way to achieve this goal. Running increases calorie burn, improves cardiovascular health, and boosts overall fitness levels. In this blog post, we will discuss how to incorporate running into your weight loss journey and important factors to consider. Additionally, we will emphasize the importance of a healthy diet, the calories burned during running, workouts, and the significance of strength training.